What to Do If Your Car's Battery Is Dead
Table of Contents
- How to get your car started when a battery is dead
- Taking your car to a service center near you
- Buying a new battery
- Jump-starting your car with another vehicle
- Using a portable jump starter
- Starting a car without electrical connections
- How to jump-start a car properly
- 6 signs your battery is failing
- When to replace your battery
- Charging and maintaining your battery at home
- Why do batteries die?
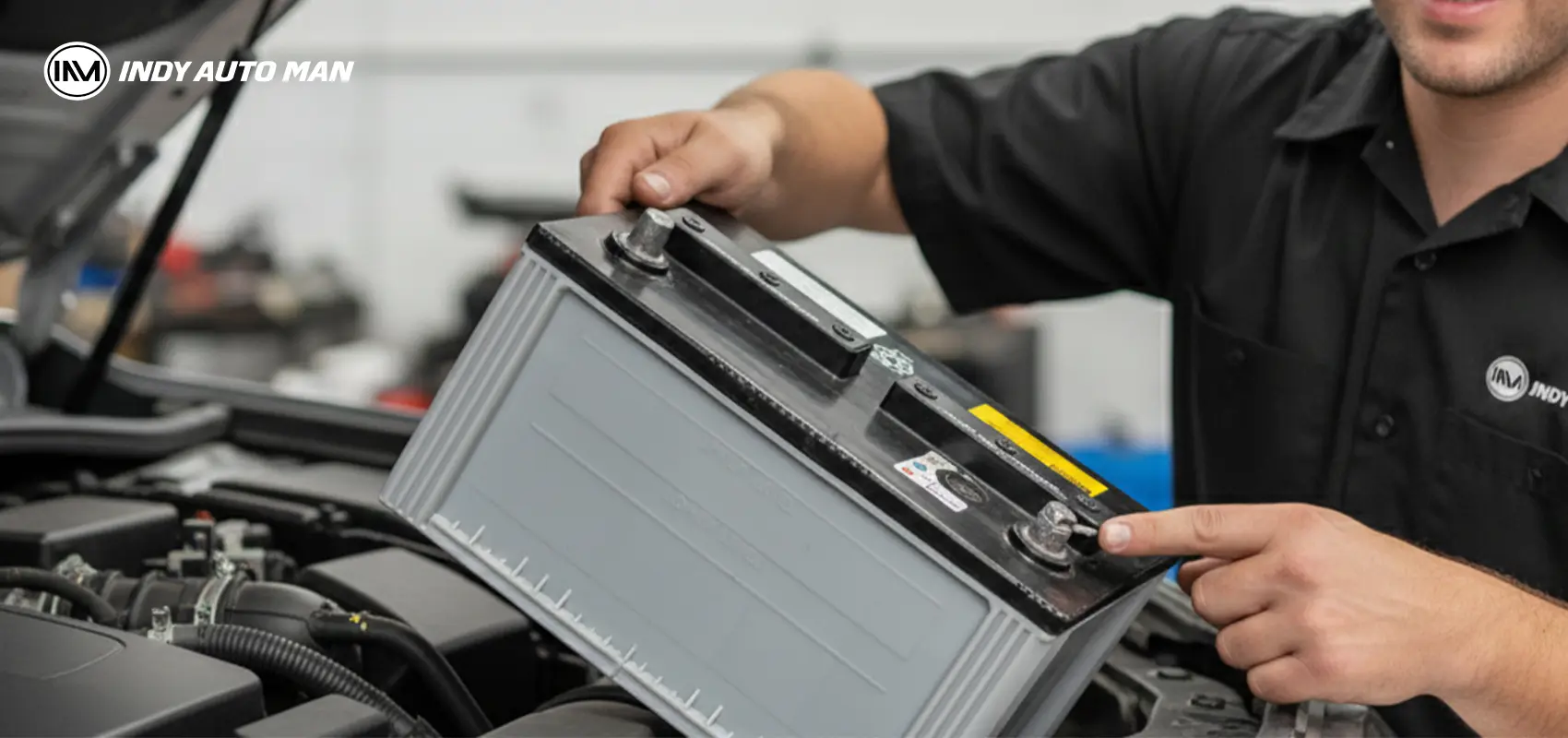

If your starter motor doesn’t turn the flywheel or does so very slowly, your car’s battery might be dead. Here are some helpful tips from our dealership’s experts on how to start a car with a dead battery, so you can still get where you need to go, like to the store to buy a new battery. First, let’s review the symptoms and causes.
How to get your car started when a battery is dead
You have several options to revive a car; they vary in cost, time, and risk.
But before trying any fixes, ensure you have your car key with you. When a dead battery is revived, it can trigger the central locking system, and if your key is still inside the car or in the ignition, it could cause more problems.
Taking your car to a service center near you
For the best and safest option, especially if you have a modern car with advanced electronics, visiting a service station is highly recommended. If you need assistance in the Indianapolis area, Indy Auto Man specialists are at your service. Expertly trained on the majority of vehicle’s makes and models, our technicians know exactly how to prevent any damage during battery diagnostics, charging, or replacement.
Battery issues often arise at the most inconvenient times, so trusting Indy Auto Man is not always an option. To avoid such inconveniences, keeping a spare battery can be reasonable for long-distance trips, just do not forget to charge it in advance.
Buying a new battery
If you prefer solving issues on the go, this can be a good choice. Take a photo of your old battery’s terminal arrangement before you rush to the store. Buying a new battery could be cheaper than towing and repairs, but only if you’re sure the battery is dead and beyond repair, such as when a cell is shorted out but the vehicle’s electrical system is intact.
If you suspect the alternator is faulty, a new battery might at least get you to a service center for proper repair. But first, try charging the battery as it might have drained naturally after sitting idle, with active security systems or electronic devices slowly consuming power.
Jump-starting your car with another vehicle
Commonly known as jump-starting, this method is quick and often effective. Using jumper cables with clamps (alligator clips), you can revive a dead battery in minutes.
However, it’s the riskiest method for both vehicles involved because incorrect procedures can cause dangerous current surges. You must follow proper safety steps, which we’ll outline below.
Using a portable jump starter
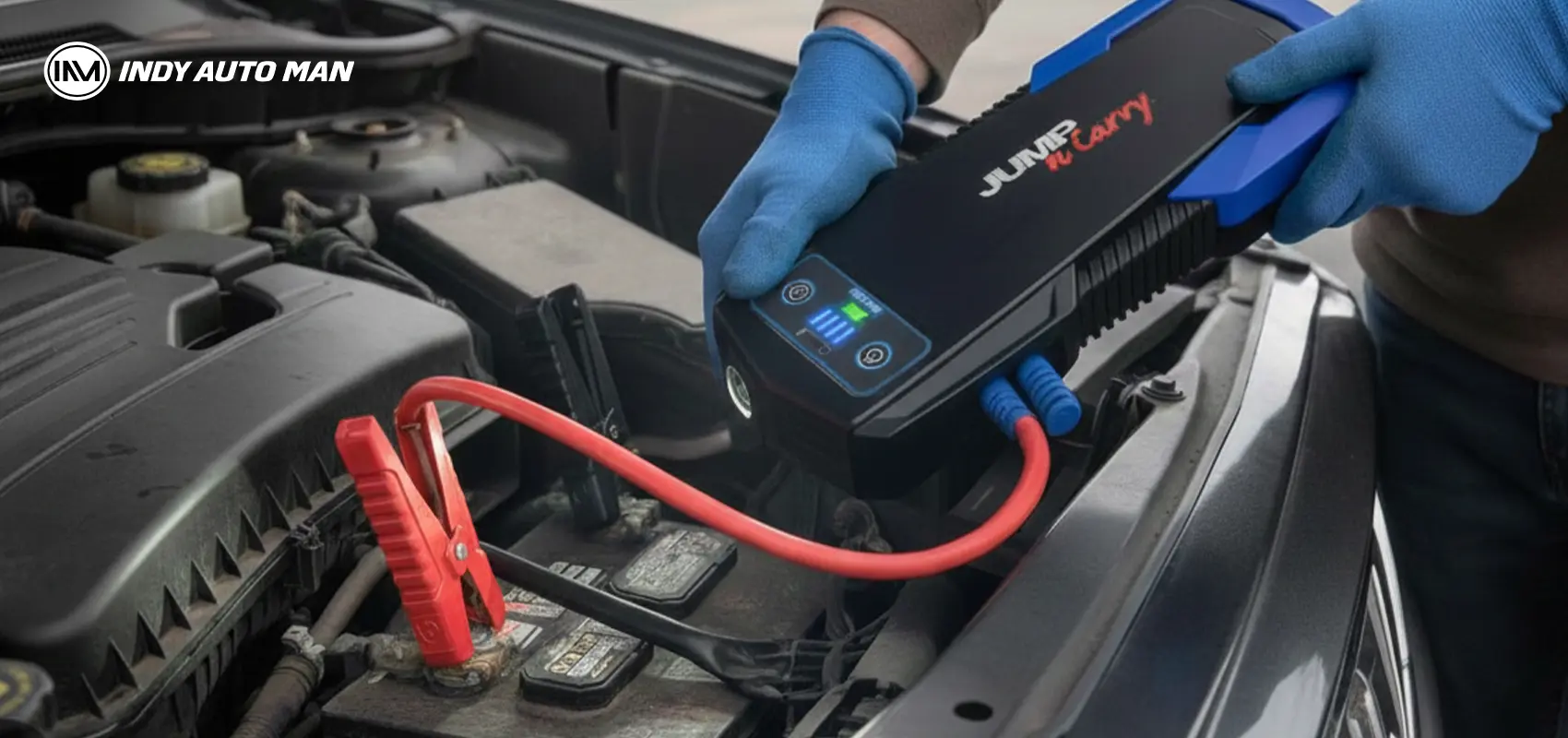

A jump starter is a device that replaces a dead battery temporarily by connecting in parallel. It’s safer than conventional jump-starting because many devices have built-in protections. The downside: high-capacity models tend to be large, expensive, and not always available when you need one.
Battery chargers and booster chargers come in several types, each with its own benefits and drawbacks:
- Transformer chargers. These devices convert 220-volt AC power into the direct current needed to charge a battery at the proper voltage. Essentially, they combine a regulated transformer with a rectifier. Transformer chargers are bulky and usually manually controlled, making them somewhat outdated today.
- Pulse chargers. Pulse chargers are lighter and more compact. They often include protections against improper connection and overcharging, and some can monitor the charging process. For example, once the battery is full, many models automatically switch to a maintenance mode with minimal current. However, carrying these in a car is impractical. They require a 220-volt power source and cannot quickly charge a battery. Their main use is for recharging batteries at home or in a garage.
- Chargers with built-in batteries. These versatile devices combine a charger with a fully functional lead-acid battery, acting like a donor car battery during jump-starts. They are excellent for maintaining voltage in a vehicle’s electrical system—for instance, when updating electronic control unit software—and can start a car even from a completely dead battery. The downside is their size and weight; these units are typically used in dealerships or repair shops. They are also expensive.
- Capacitor jump starters. These are more portable jump starters that store energy in capacitors, which release power to start the engine. They can plug into a 220-volt outlet but shine for their ability to work standalone without nearby power. Compact and handy, they can start an engine or recharge a slightly discharged battery in a parking lot or driveway. Cheaper models offer enough charge for two or three reliable starts but are not suitable for fully and safely charging significantly drained car batteries.
- Power banks for cars. These resemble the portable chargers used for phones and laptops, but are larger and designed for 12-volt vehicle systems. While a power bank can’t replace a heavy lead-acid battery or bring back a completely dead battery, it can revive it enough to start the engine.
Today, you can easily find power banks equipped with alligator clips and capacities up to about 20,000 mAh. Their versatility lets them also charge laptops or smartphones. However, they can cost as much as a new car battery. So often, buying a new battery is simpler.
Starting a car without electrical connections
If your battery still powers the ignition and fuel pump but isn’t fully charged, you might try “bump starting” or “push starting” the vehicle. This means towing the car or pushing it with a few people to get it moving, then engaging the clutch to start the engine via the rotating wheels.
However, this method only works for manual transmission vehicles and can damage modern engines equipped with fuel injection and catalytic converters. It also puts strain on the timing belt or chain, sometimes causing failure under the sudden force.
How to jump-start a car properly
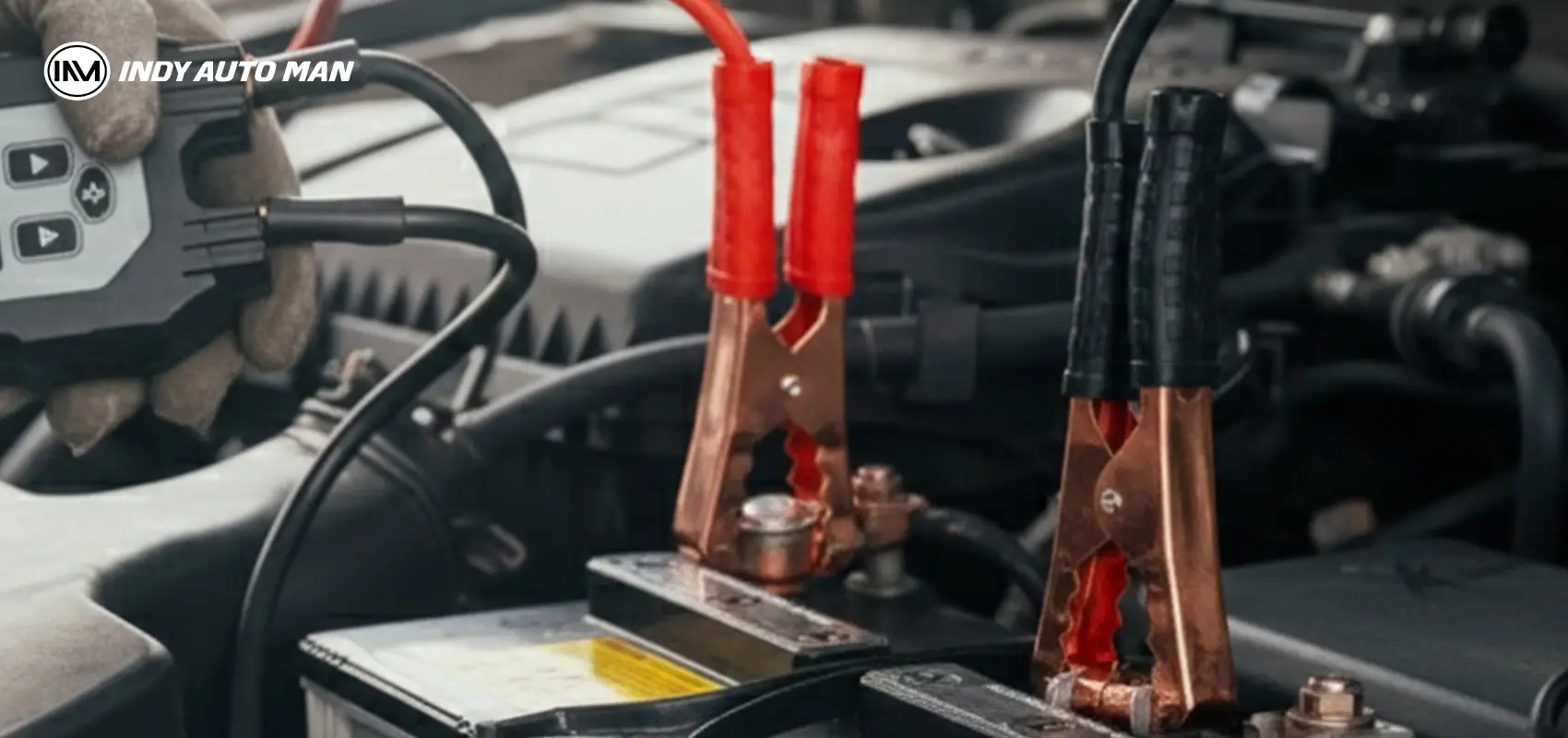
Many car owners in Indiana with electronically managed engines hesitate to jump-start due to fears of damaging electronics. But if done carefully, jump-starting is safe and is even described in modern owner’s manuals.
Important: Do NOT jump-start a 12-volt car battery using a 24-volt truck battery.
Steps for safe jump-starting:
- Use good-quality jumper cables, long enough to connect both cars with good insulation and tight, toothed clamps. Ideally, positive (red) and negative (black) cables should be color-coded to avoid mistakes.
- Park the working vehicle close enough for cables to reach. If your battery is under the trunk, use special jump-start terminals located under the hood.
- Turn off the engine and ignition of the working car before connecting any cables to prevent voltage spikes.
- First, connect the red positive cable: clamp one end to the donor car’s positive terminal, then the dead car’s positive terminal.
- Next, connect the black negative cable: one end to the donor car’s negative terminal and the other to an unpainted metal ground on the dead car away from the battery.
- If the dead battery is only slightly drained, wait a few minutes, then try to start the car.
- If more charge is needed, start the donor car and run it for 5 to 10 minutes at slightly higher RPM to allow the alternator to provide a stronger charge.
- Turn off the donor car's engine before you attempt to start the dead one again.
- Once the dead car starts, carefully remove cables in reverse order, making sure they don’t touch metal parts or each other.
- Let your engine idle for a few minutes. Driving will recharge the battery faster since the alternator generates more current at speed.
Remember, modern batteries are high-capacity and won’t fully recharge after a short run. After an emergency starting, it’s best to visit a service center or recharge the battery fully.
6 signs your battery is failing
- Exterior lights appear dimmer than usual.
- Central locking/keyless entry stops working.
- Dashboard lights dim when turning the key.
- The starter motor spins slowly or makes a rough sound.
- Clicking noise instead of engine cranking.
- No response when turning the ignition key - no lights or sounds.
More expensive, tech-heavy cars often face higher costs and complications when batteries fail.
When to replace your battery
Batteries wear out faster with:
- Off-road or rough driving
- Lack of maintenance
- Poor or unqualified electrical repairs
- Deep discharges or frequent undercharging
Even with perfect care, batteries degrade eventually. Replace your battery if the terminal voltage dips below 12 volts when the engine is off or if starting becomes difficult even after a short rest.
Charging and maintaining your battery at home
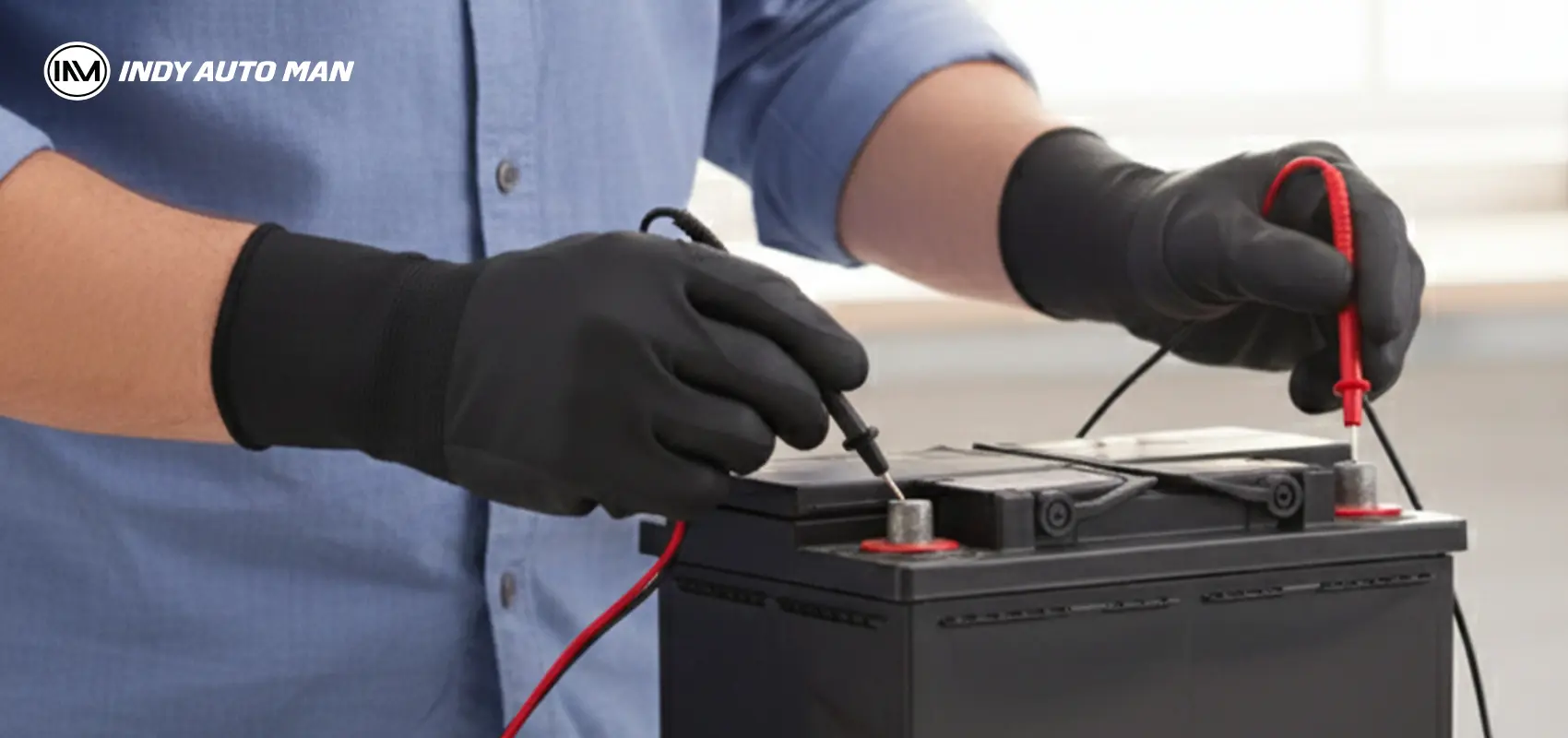

Most modern batteries are maintenance-free. To extend battery life:
- Avoid overloading electrical systems with unnecessary equipment.
- Use an insulated battery warmer case in cold weather when possible.
- Keep battery terminals clean.
- Regularly clean the battery casing to prevent self-discharge.
Recharging is critical after long periods of inactivity or short trips in winter, when the alternator can’t fully replenish power used by starters and electronics.
Why do batteries die?
Modern batteries usually last about 5 years, with many lasting 8 to 10 years. They fail due to:
- Plate sulfation (hard deposits forming);
- Electrolyte boiling over;
- Lead plate shedding causing shorts;
- Natural discharge through the casing.
Battery capacity slowly decreases, and self-discharge increases until it can't start the engine.
Other common battery killers include:
- Electrical system faults: shorts, corroded contacts, or electronics left on.
- Forgotten lights or devices draining power overnight.
- Alternator failure, indicated by a battery warning light, causing quick battery drain.
- Cold weather which reduces battery capacity.
If you’re dealing with battery issues or need expert help selecting the right charger or replacement battery, don’t hesitate to schedule a visit to the Indy Auto Man service station in Indianapolis. Our experienced technicians provide fast diagnostics, battery testing, and professional installation to get you back on the road quickly and safely. Contact us today at Indy Auto Man to book your appointment and keep your vehicle running smoothly all year round.
